Heating Applications in Dairy Heat Exchangers
Heat Exchangers
The use of heat exchangers in dairy heating allows for precise temperature control, which is critical during pasteurization where milk is heated to kill pathogens while preserving nutrients.
Pasteurization Heating
During dairy processing, milk must be heated to specific temperatures for pasteurization. Plate heat exchangers are known for their high heat transfer efficiency and compact form factor, and are often employed in this step. They enable fast and uniform heating of the milk, ensuring effective pathogen reduction while maintaining quality.
Subsequently, controlled heating is achieved through carefully managed heat application provided by heat transfer systems. After this, precise temperature control with heat exchangers is necessary to prepare the product for further processing, preventing bacterial growth and ensuring optimal conditions.
UHT Heating
In ultra-high temperature (UHT) processing, the heat exchanger is equally important. The control of temperatures influences the sterilization of milk, directly affecting shelf life and taste. The energy efficiency of heat exchangers, often using recovered heat from other stages, reduces operational costs. Heat exchangers ultimately heat milk to high temperatures for short times, delivering sterility and extended shelf life with their exacting temperature control.
Industry-grade heat exchangers are designed to withstand the demanding environment of dairy plants, where acidic conditions and high-temperature swings can challenge equipment. These exchangers' durability stands up to the rigorous cleaning chemicals essential for maintaining hygiene standards without compromising integrity.
In dairy production, heat exchangers are more than just equipment; they are central to the science of dairy processing, affecting everything from efficiency and cost-effectiveness to the quality of the final product. Their value in heat management and energy recovery can't be overstated, making them indispensable in the dairy industry.
Precise Temperature Control
The heating of dairy products to stabilize and process them before packaging is another stage where heat exchangers play a key role. Advanced temperature changes performed by these exchangers ensure that products reach the needed conditions without compromising quality or flavor.
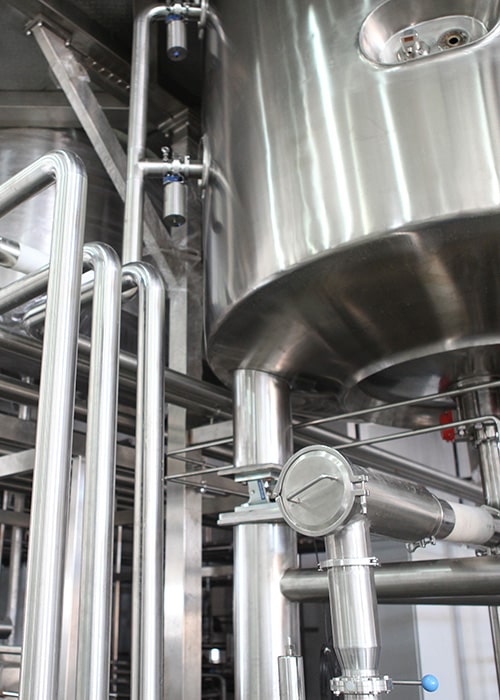

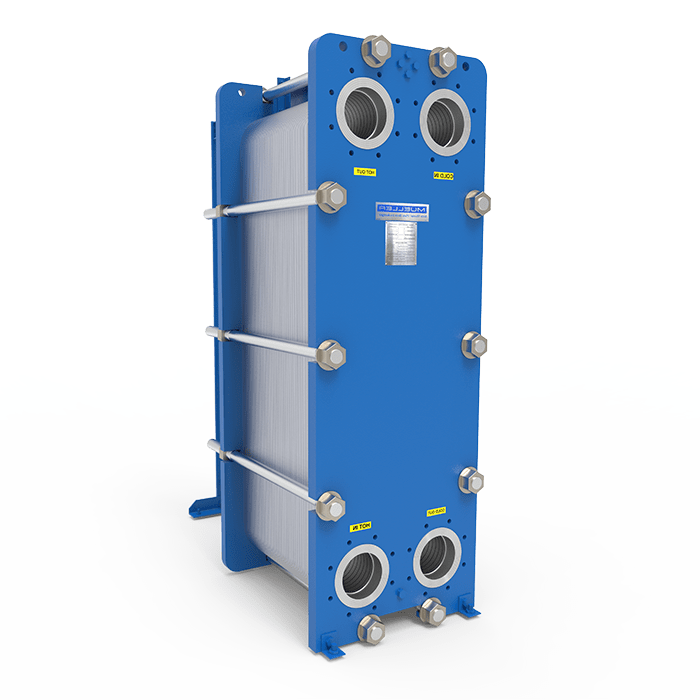
Plate & Frame Exchangers
Compact High-Efficiency Heating & Cooling
- Up to 10,000 L/h Capacity
- Regenerative Energy Recovery
- CIP-Compatible Gaskets
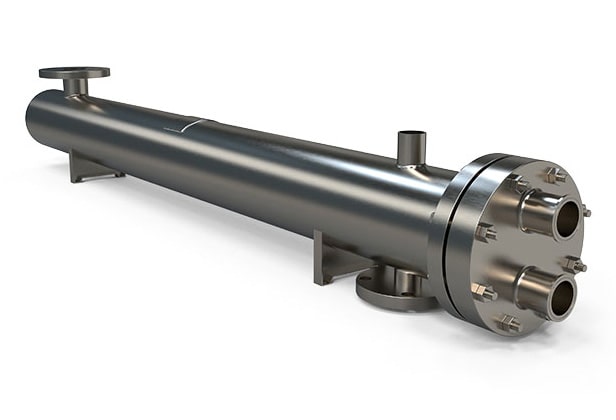
Shell & Tube Exchangers
Robust for Viscous Milk Flows
- Custom Tube Configurations
- High-Pressure Handling
- Sanitary Tri-Clamp Fittings

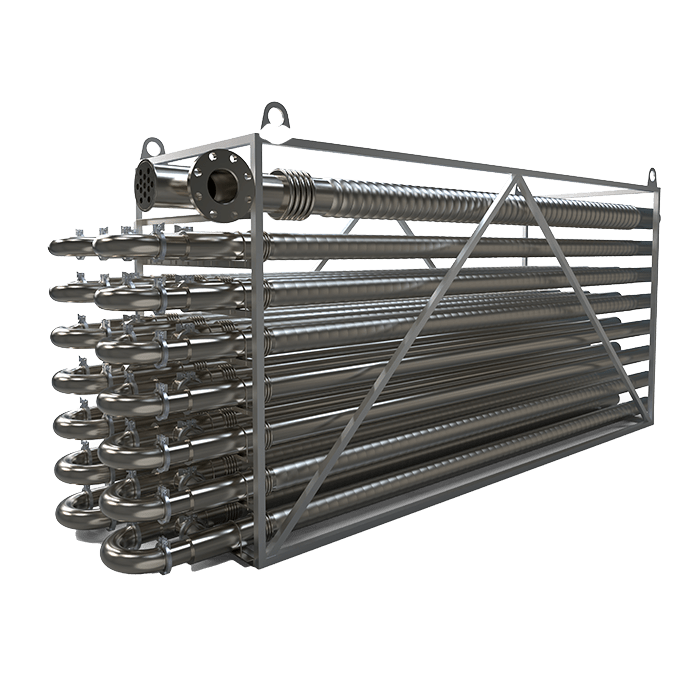
Tube-in-Tube Exchangers
Gentle, Low-Fouling Heat Transfer
- Coaxial Tube Design
- Ideal for Pre/Post-Homogenization
- Fully CIP & 3-A Compliant
Advantage Chillers
Precision Cooling to 0.5°C
- Water or Glycol Systems
- ±0.1°C Temperature Stability
- Stainless Steel & CIP Ready



